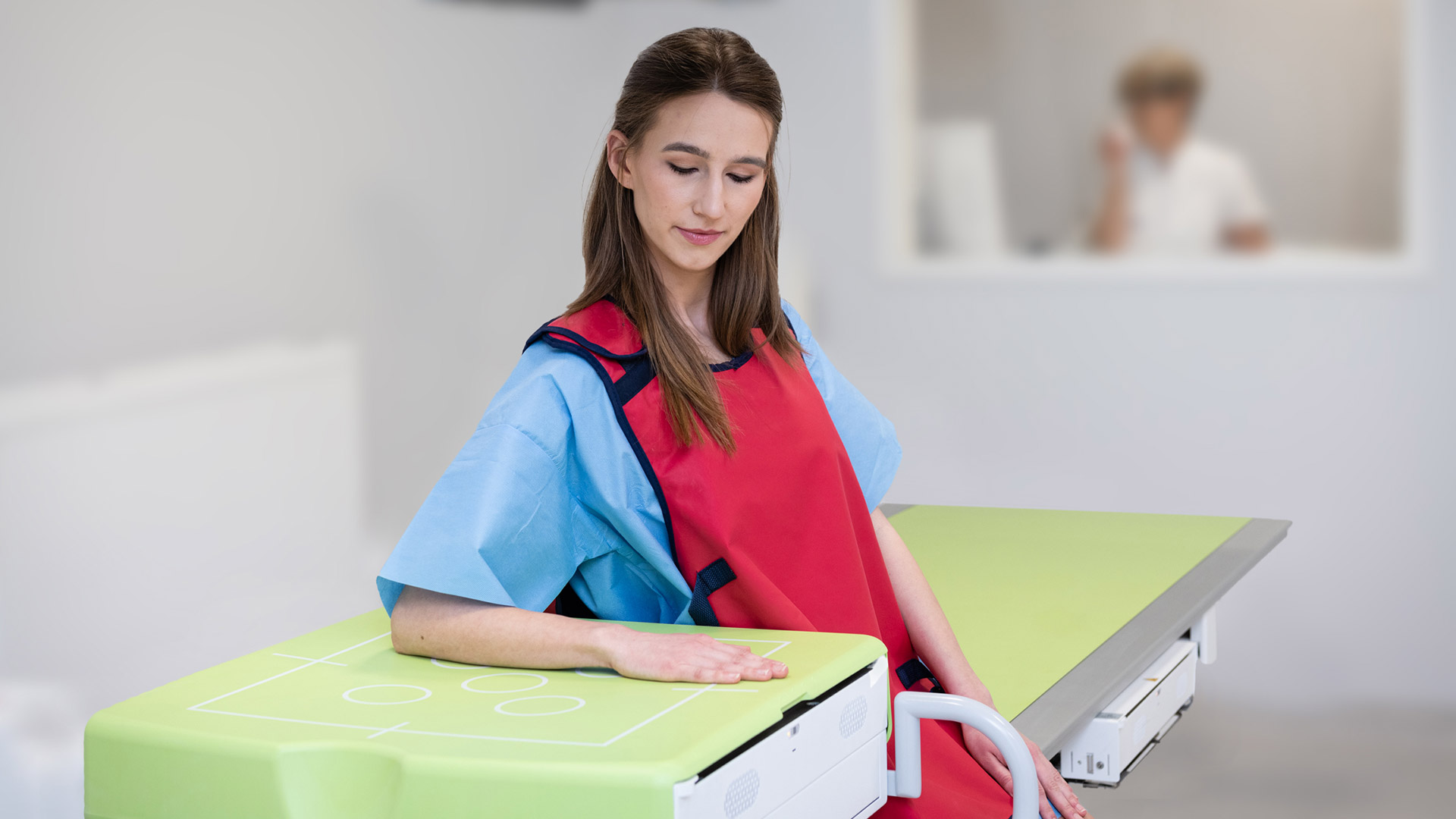
X-ray examination is an imaging technique that uses x-ray wavelengths. It is the basic method of imaging the skeletal system due to its wide availability, relatively low cost, and short examination time. X-rays have been a very well-known and safe technique used in medicine for over 100 years.
At the Carolina Medical Center, two modern Philips Digital Diagnost devices (Eleva and C90) are used for X-ray examinations. Both devices are configured in such a way as to make it as easy as possible for patients to perform the examination, and by using modern digital techniques, to reduce the dose of radiation.
Based on the X-ray image, the structure of the bone tissue is assessed – e.g., possible cracks and fractures. Treatment can be planned and healing progress monitored by means of X-ray in most patients with bone trauma. X-rays cannot be used to assess other tissues, such as ligament or muscle injuries. The X-ray examination only shows the outline of the soft tissues, not the structureę.
Indications for X-ray examination
The indications for X-ray examination are assessed by a doctor each time and they can only be performed based on a valid referral (the elements that must be included in the referral are described in the Act). The spectrum of the possibilities of this examination is very wide. It is usually done in the case of pain in a limb or joint after an injury. In such cases, the purpose of this examination is to detect, for example, a bone fracture and provide appropriate treatment on this basis.
However, the indications for this examination are not limited to injuries only. X-ray examinations are also used to assess the axis of the limbs and the position of the bones (e.g., in the joints of the feet and wrists). Thanks to the radiological assessment of the angles and position of the bones, we can diagnose significant ligament injuries. In such cases, the bone structure is unchanged and only an experienced radiologist or orthopedist can detect subtle but significant pathologies.
A very important role of X-ray examinations is also in the assessment of all other pathologies of the skeletal system, such as the advancement of degenerative changes or joint inflammation in the course of systemic or metabolic diseases.
The scope of performed X-ray examinations
The X-ray machine at the Carolina Medical Center is used for:
- general diagnostic tests (e.g., chest examination),
- skeletal system examinations in standard and complementary projections (e.g., Merchant, mortis, West-Point and “Y” views),
- examinations of the entire spine and the entire lower limbs using digital image merging,
- functional tests (e.g., of the spine),
- stress tests using the TELOS device,
- stress tests – e.g., testing the feet while standing on toes.
In our clinic, we perform a full range of X-ray examinations, which are used in the diagnosis of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. We also perform a postural X-ray of the lower limbs, covering the entire lower limbs,, including the hip, knee and ankle joints. This examination allows to assess axis disorders and asymmetry of limb length.
We often perform comparative X-ray examinations of the limbs, which significantly increases the accuracy of the examination and facilitates the detection of pathologies, especially in our youngest patients.
We provide:
Preparation for X-ray examination
Most X-ray examinations do not require special preparation – you can eat and drink, take medications, and take up daily activities.
women of childbearing age should undergo X-ray examinations during the first 10 days of the menstrual cycle, as the probability of becoming pregnant during this period is lower, a pregnant woman, before performing an X-ray examination, must notify of this fact the attending physician, the receptionist who enrolls for the examination, and the person performing the examination, for the X-ray examination, please wear white underwear without prints, clasps or decorative hooks.
However, you should prepare for an X-ray of the lumbar spine, sacroiliac joints, and the abdominal cavity.
On the day before the X-ray examination:
- take Espumisan 3 x 2 capsules (intestinal laxative should be taken in the afternoon),
- do not eat hard-to-digest or flatulent foods, i.e., fresh vegetables, fruit, bran, groats, dark bread,
- and do not drink carbonated liquids, only drink clear and unsweetened liquids – non-carbonated mineral water, tea, coffee.
On the day of the X-ray examination, when we perform the examination in the morning:
- take Espumisan 1 x 2 capsules,
- you should be on an empty stomach (only water needed to drink the above-mentioned drugs is allowed),
- you should not smoke cigarettes or chew chewing gum.
On the day of the X-ray examination, when the examination is performed in the afternoon:
- take Espumisan 3 x 2 capsules,
- do not eat anything 6 hours before the test, and prior to that, only light foods – see the diet on the day before the test described above,
- you should not smoke cigarettes or chew chewing gum.