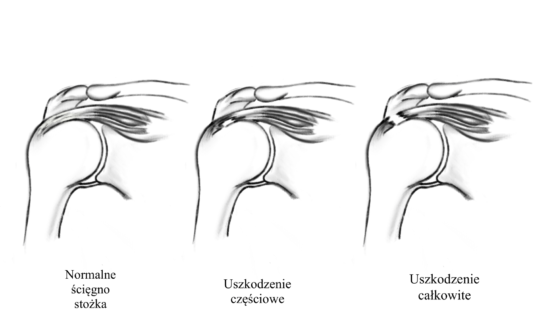
Diagnosis
An initial diagnosis can be given on the basis of the consultation and clinical examination. However, imaging tests – magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or ultrasound are necessary to confirm the type and degree of tear.
Treatment of rotator cuff tear
Treatment of a rotator cuff tear depends on the patient’s age, activity, degree of injury (partial or full-thickness tear) and the type of injury (acute / chronic).
Conservative treatment is successfully applied in the case of chronic and partial-thickness tears and in people over 70 years of age. It involves modification of activity and rehabilitation aimed at restoring functions of the joint.
An important element of treatment is the periodic administration of oral anti-inflammatory drugs and intra-articular injections:
- corticosteroids – temporarily reducing pain, allowing for gradual rehabilitation exercises;
- platelet-rich plasma – PRP (blood taken from the patient is subjected to a special process, resulting in a concentrated mixture of proteins and growth factors) – it modulates the inflammatory and analgesic process.
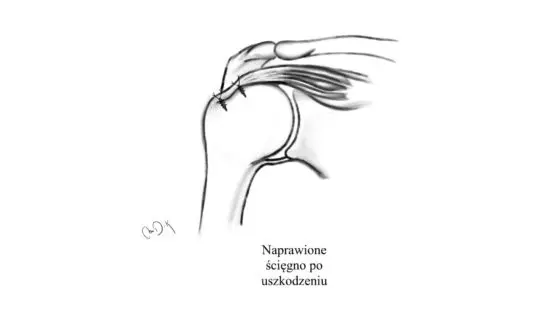
Surgical treatment of rotator cuff tear is indicated in acute injuries and for patients who underwent conservative treatment and it did not bring the expected results or for people under 60 years of age.